Orthopedic Surgery

Introduction
At our department, we strive to alleviate pain and restore function of the musculoskeletal system—including bones, muscles, and joints—so that patients can improve their quality of life more quickly and effectively.
We provide medical care with careful consideration not only of each patient’s condition, but also their individual preferences, values, family situation, and social background, aiming to offer the most suitable treatment for every patient.
Even if you are uncertain about the timing or method of treatment, please feel free to consult with us.
Characteristics of this department
①Robot-Assisted Surgery
- We perform robot-assisted total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
- With the support of a computer-controlled robotic arm, we can shave the damaged bone more precisely and safely than with conventional methods. This results in highly accurate placement of the artificial joint.
- As a result, patients can expect better early functional recovery, reduced postoperative pain, and potentially longer-lasting artificial joints.
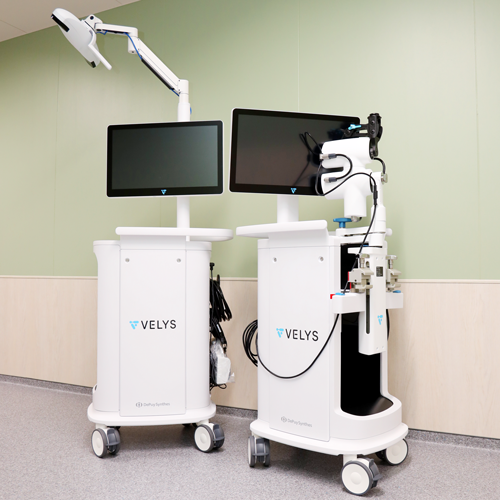
VELYS
Robotic System for Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)
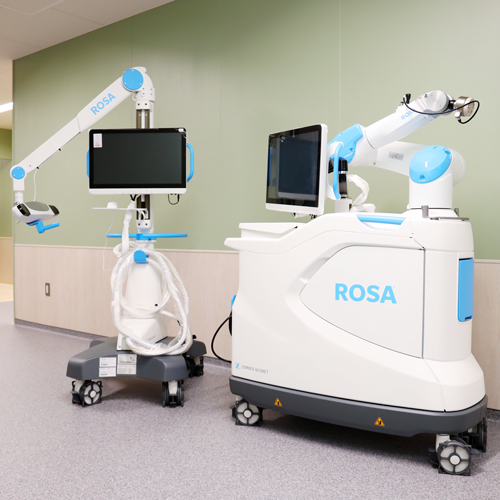

ROSA
Robotic System for Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA)
Surgical Robots Used in Our Department
- VELYS – Robotic System for Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)
- Robotic System for Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)
This system enables bone cutting with an accuracy of 0.5 mm and 0.5 degrees (compared to the 1–2 mm and 2–3 degrees precision of conventional techniques).
Intraoperative simulation helps minimize ligament detachment, leading to faster postoperative recovery.
- Robotic System for Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)
- • ROSA – Robotic System for Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA)
- Robotic System for Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA)
Enables implant positioning with precision to the nearest degree.
Leg length discrepancy can be identified and corrected with 1 mm accuracy during surgery, reducing previously undetectable errors.
- Robotic System for Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA)
②Minimally Invasive Total Hip Arthroplasty (MIS THA)
Using the Direct Anterior Approach (DAA) and robotic assistance, we perform safer and less invasive surgeries than traditional methods.
Depending on preoperative walking ability, some patients are able to be discharged within approximately one week.
③Efforts to Minimize Waiting Time in Trauma Care
- We are committed to minimizing waiting time for patients requiring trauma care.By performing early surgery and initiating early rehabilitation, we aim to prevent complications and disuse syndromes such as muscle weakness and joint contracture. This approach also facilitates an earlier return to daily life and social activities.
- For femoral neck fractures, we perform hemiarthroplasty using the Direct Anterior Approach (DAA).
Compared to the traditional posterior approach, the anterior approach is less invasive and allows for faster recovery. In addition, it significantly reduces the risk of dislocation, meaning that postoperative rehabilitation and daily activities can proceed with minimal restrictions—an important benefit for patients.
④Regenerative Therapy
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy(Self-funded treatment)
- PRP therapy involves drawing 20 to 50 mL of the patient’s own blood and processing it with a specialized device to extract the portion rich in platelets—called Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP).
PRP contains a high concentration of growth factors, which play a key role in promoting tissue repair. - By injecting PRP into the affected area, tissue healing is accelerated, which can lead to pain relief and faster recovery.
- This treatment is commonly used for osteoarthritis of the knee and ligament or muscle injuries caused by sports or physical activity.


Main diseases
- Osteoarthritis of the Hip
- Osteoarthritis of the Knee
- Femoral Neck Fracture / Intertrochanteric Fracture of the Femur
- General Trauma (Fractures and Dislocations)
- Sports-Related Injuries
- Osteoporosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Treatment
We have introduced clinical pathways for inpatient treatment of aspiration pneumonia, urinary tract infections, dehydration, etc. This involves creating a plan for treatment (infusions, antibiotic drips, etc.) and examinations (blood tests, X-rays, etc.) for each illness from admission to discharge, and then proceeding with treatment according to that plan. We believe that this will lead to standardization of treatment and shortened hospital stays, allowing patients to receive better medical care.
Outpatient schedule
Morning 9:00~12:00(Reception8:00-11:30)/
Afternoon to Evening 13:30~16:30(Reception13:00-16:00)
| Mon | Tue | Wed | Thurs | Fri | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Afternoon to Evening | - | - | - | - | - |
Medical track record of the clinical department
-
Surgical method Number of procedures Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 1 (Femur) 262 Hemiarthroplasty – Type 1 (Hip) 221 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 1 (Humerus) 92 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 2 (Lower Leg) 75 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 2 (Forearm) 66 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 3 (Clavicle) 35 Temporary External Fixation for Fracture Treatment 25 Removal of Internal Fixation Device – Other Locations 24 Removal of Internal Fixation Device – Type 2 (Forearm) 21 Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) – Type 1 19 Removal of Internal Fixation Device – Type 2 (Lower Leg) 19 Wound Management / Wound Closure Procedure 10 Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) – Type 1 9 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 3 (Patella) 9 Limb Amputation – Type 2 (Thigh/Femur Level) 8 Removal of Internal Fixation Device – Type 1 (Femur) 8 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 3 (Digits – Hand or Foot) 7 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 3 (Foot) 7 Percutaneous Pinning (Pin Insertion) 7 Removal of Internal Fixation Device – Type 3 (Patella) 7 Intra-articular Fracture Repair – Type 1 (Knee) 6 Removal of Internal Fixation Device – Type 1 (Humerus) 6 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 3 (Hand, excluding Scaphoid) 5 Removal of Internal Fixation Device – Type 3 (Digits – Hand or Foot) 4 Tendon Sheath Release (Tenosynovotomy) 4 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 1 (Scapula) 3 Open Reduction of Joint Dislocation – Type 1 (Hip) 3 Removal of Intra-articular Foreign Body – Type 2 (Elbow) 3 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) for Pelvic Fracture 3 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for Iliac Wing Fracture 3 Ligament Reconstruction Surgery 2 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Type 3 (Other Locations) 2 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for Acetabular Fracture 2 Arthroscopic Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for Intra-articular Fracture (Elbow) 2 Removal of Intra-articular Foreign Body – Type 1 (Hip) 2 Removal of Intra-articular Foreign Body – Type 2 (Foot) 2 Intra-articular Fracture Repair – Type 1 (Elbow) 2 Intra-articular Fracture Repair – Type 2 (Hand) 2 Intra-articular Fracture Repair – Type 2 (Foot) 2 Removal of Internal Foreign Object (Implant) from Pelvis 2 Removal of Internal Fixation Device – Type 3 (Hand) 2 Nerve Repair – Type 2 (Other Locations) 2 Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) 2 Excision of Subcutaneous or Skin Tumor 2 Open Mobilization Procedure – Type 2 (Sternoclavicular, Elbow, Hand, Foot) 1 Total Shoulder Arthroplasty – Type 1 1 Removal of Central Venous Port (CV Port) 1 Dupuytren’s Contracture Surgery 1 Removal of Wire or Similar Fixation Material (Under Anesthesia) 1 Debridement for Pyogenic or Tuberculous Arthritis (Shoulder) 1 Arthroplasty (Joint Reconstruction) – Knee 1 Joint Incision and Drainage – Type 1 (Hip) 1 Open Reduction of Joint Dislocation – Type 2 (Hand) 1 Surgery for Pseudarthrosis (Hand, excluding Scaphoid) 1 Pseudarthrosis Surgery – Type 1 (Scapula) 1 Pseudarthrosis Surgery – Type 2 (Lower Leg) 1 Pseudarthrosis Surgery – Type 2 (Forearm) 1 Pseudarthrosis Surgery – Type 3 (Hand) 1 Rotator Cuff Repair (Simple Procedure) 1 Pelvic Osteotomy 1 Amputation at Joint Level – Digits (Hand/Foot) 1 Lower Leg Amputation 1 Open Reduction of Extensor Tendon Dislocation (Digit) 1 Removal of Internal Fixation Device – Type 3 (Foot) 1 Endoscopic Neurolysis 1 Nerve Repair – Type 1 (Digits of Hand or Foot) 1 Hemiarthroplasty – Type 1 (Shoulder) 1 Ligament Repair for Rupture 1 Full-Thickness Skin Graft 1 Stump Formation – Bone – (Finger) 1 Closed Reduction of Fracture (Non-Operative) 1 Scar Contracture Release Surgery 1 Tendon Grafting Surgery 1 Tendon Release Surgery 1 Tendon Repair (Digit) 1 Ligament Repair – Other Ligaments 1 Total number of medical departments 1043 -
Anesthesia method Number of cases General Anesthesia 1001 Conduction Anesthesia (Nerve Block) 252 Spinal Anesthesia 54 Epidural Anesthesia 34 Local Anesthesia 18 No Anesthesia 1 Total number of medical departments 1400
Regarding clinical research
Click here for more information on clinical research

